Treatment for a stroke by the method of professor Smikodub
A stroke, regardless of its origins, is mostly considered as an acute attack, which is based on a blood supply violation to the brain. The presence of severe neurological symptoms and a number of consequences prescribes a long course of recovery for patients.
Classical medical treatment of a stroke is directed to improving the general condition and minimizing the manifestation of cognitive dysfunctions, which are most often observed in patients of this category. Unfortunately, the drugs used, as well as rehabilitation techniques, mainly aimed at the patient's adaptation to a common lifestyle, cannot affect the primal cause of development of the disease - the damaged brain area after hemorrhage or blood supply disturbance.
Risk factors and mechanism of acute stroke development
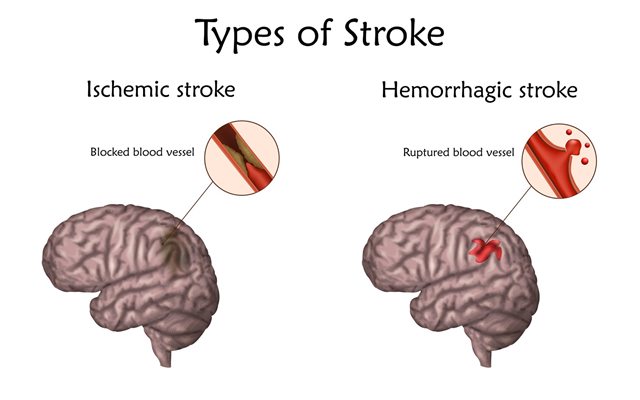
It is usually not possible to predict the onset of an attack and to carry out its primary prevention. it can be provoked by a lot of diseases at various stages of their development. Some of them progress for many years and become the reason for the cessation or violation of the blood supply to a certain part of the brain - ischemia, and as a result, an ischemic stroke occurs. Such pathologies include:
• Arterial hypertension;
• Vasculitis;
• Atherosclerosis;
• Hyperlipidemia;
• Thromboembolism of cerebral arteries and veins;
• Ischemic heart disease;
• Diabetes mellitus;
• Arrhythmias.
A decrease in blood flow leads to a cascade of metabolic reactions that stimulate an increase in the concentration of toxic substances (Glutamic acid, Calcium, Nitrogen) in the cells of the brain tissue - neurons, after that — inflammatory reactions occur, and edema develops. The integrity of the vascular wall is also disrupted, the blood-brain barrier is damaged - the physiological barrier between blood and tissue fluid in the central nervous system, which causes the accumulation of anaerobic glycolysis products in the damaged area. All of the above processes ultimately lead to the death of neurons and the formation of cerebral infarction zone; the severity of a particular function’s violation depends on the localization of a latter.
Also, the mechanism for the development of an acute blood supply violation can be a sudden hemorrhage in the brain as a result of rupture of one or more cerebral vessels - a hemorrhagic stroke develops. As a rule, many predisposing diseases, characterized by damage to the vascular wall in the later stages, contribute to its occurrence:
• Arterial hypertension;
• Arrhythmias preceding the formation of blood clots;
• Atherosclerosis;
• Intracranial aneurysm formation;
• Septic artheritis;
• Diabetes;
• Vasculitis.
In addition to the described diseases of the cardiovascular system, hemorrhage can occur after trauma and severe concussion of the brain, as well as rupture of a vessel when it is affected by metastasis of a tumor of various locations. A sudden violation of the blood flow into one of the brain parts - the formation of a hemorrhagic focus immediately entails the development of edema and an increase in intracranial pressure. The permeability of the blood vessels’ wall also increases, which leads to the release of blood plasma outside it - an imbalance between coagulative and anti-coagulative systems of the blood develops. All the pathological changes described above cause the death of neurons in the damaged area of the brain.
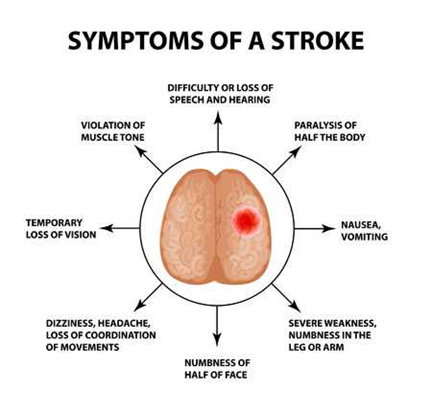
Symptoms of an attack develop almost immediately after an acute disturbance of blood supply:
• speech disorder;
• headache;
• dizziness;
• paresis (decreased muscle strength) of one of the body parts;
• paralysis (complete absence of muscle biomechanics);
• space disorientation;
• loss of consciousness;
• violation of higher nervous activity functions;
• loss of vision.
The consequences of a stroke (long-term preservation of one or more of the listed symptoms) almost always require a long-term rehabilitation and adherence to a completely new way of life, full of restrictions.
For such patients, it is of great importance to restore the impaired body functions by directly affecting the primary (ischemic or hemorrhagic) focus of the disease in the brain.
In addition to the described diseases of the cardiovascular system, hemorrhage can occur after trauma and severe concussion of the brain, as well as rupture of a vessel when it is affected by metastasis of a tumor of various locations. A sudden violation of the blood flow into one of the brain parts - the formation of a hemorrhagic focus immediately entails the development of edema and an increase in intracranial pressure. The permeability of the blood vessels’ wall also increases, which leads to the release of blood plasma outside it - an imbalance between coagulative and anti-coagulative systems of the blood develops. All the pathological changes described above cause the death of neurons in the damaged area of the brain.
The origin of fetal stem cells and their mechanism of action on the nervous system
In the Unique Cell Treatment Clinic under the leadership of Professor Smikodub, a method of using fetal stem cell preparations has been developed to ensure the restoration of the function of the nervous system and the integrity of the brain structures. No matter how frightening the manifestations of a stroke would be, treatment and recovery after it under the clear guidance of our specialists will maximally help to return the patient to a previous life.
Fetal stem cells are the only source of natural neuroectoderm stem cells - precursors of neurons. Their use in the treatment of neurological diseases is most effective, compared to other types of stem cells. They have the exceptional property of giving rise to new neurons, giving the biological material for building healthy nerve tissue. As a result, the nerve tissue acquires new opportunities for growth and regeneration, reducing the area of brain damage. The drugs, based on fetal stem cells, promote the secretion of a large number of growth factors, that lead to active differentiation of neuronal progenitor cells and maintenance of new neurons' growth. Thus, in the newly built brain tissue, all violated metabolic processes are restored and accumulation of pathological elements in it becomes impossible.
Also, one of the essential characteristics of our fetal stem cell preparations, which plays a key role in the treatment and prevention of recurrent strokes, is initiation of neoangiogenesis - the process of new vessels formation. This happens by stimulating of the production of two protein types: fibroblast growth factor and vascular endothelial factor. In a healthy organism, their moderate secretion occurs throughout life, but, as a rule, is happens to maintain the normal flow of metabolic substances with the blood to the brain. Fetal stem cells, upon entering the body, activate the production of these proteins in greater quantities, compared to the norm, and affect their additional function - the full-valued construction of the vascular wall and formation of new vessels, by reorganizing the primary ones and making them more resistant to external damaging factors.
The results of the stem cell therapy course in the Unique Cell Treatment Clinic
Treatment in our clinic according to the method of Professor Smikodub leads to a significant improvement in the condition of patients - an achieved effect is much superior to other modern methods:
• recovery of muscle biomechanics and improvement of motor functions;
• improved speech, coordination, and spatial orientation;
• positive effect on mental disorders, including depression, improvement of social skills;
• recovery of short-term and long-term memory;
• return and improvement of cognitive functions;
• vision recovery.
Improvements in the general condition of the patient are visible after the first course of drug administration. Proper observance of all recommendations and passage of a fully prescribed course will minimize the manifestations of stroke and allow the patient to live without former restrictions. Cellular treatment in most cases is easily tolerated by the patient and, depending on the severity of the condition, takes from 3 to 5 days; with the course of neurological rehabilitation — up to 14 days.
