Diabetes treatment with stem cells

Diabetes mellitus is a chronic systemic endocrine disease developing as a result of an absolute or relative insulin deficiency, the main manifestation of which is a persistent increase of blood glucose levels (hyperglycemia), leading to metabolic disorders in the body.
Type 1 diabetes mellitus, which occurs mainly among children and adults up to 40 years, is a genetically determined disease and is characterized by an "absolute" deficiency of the hormone insulin. Insulin secretion decreases due to the massive destruction of the endocrine cells of Langerhans islets of the pancreas. Death of β-cells of the pancreas, in most cases in the type 1 diabetes mellitus, is caused by an autoimmune process, whereby the human immune system excretes antibodies against the body's own cells, destroying them, and may also occur in case of pancreatitis, viral infections, toxic lesions of the pancreas and oncological diseases.
Type 2 diabetes mellitus is characterized by a "relative" insulin deficiency, when insulin is produced in a normal amount, but it is violated its interaction with body’s cells and its normal concentration in blood does not provide an adequate carbohydrate metabolism. Mostly people over 40 years old suffer from this type of diabetes. The main causes of insulin resistance are: change of qualitative characteristics of the insulin, disturbance of function of insulin receptors on the membranes of insulin-dependent cells or intracellular mechanisms changes, accelerated process of its destruction. In the heart of development of type 2 diabetes is also a genetic predisposition, which occurs under the influence of risk factors such as age, obesity, smoking, alcohol drinking, chronic overeating, lack of exercise, high blood pressure and others. Diabetes leads to disruption of all types of metabolism (carbohydrate , lipid, protein and water- electrolyte metabolism), resulting in metabolic disturbance of all human tissues, eventually develop severe complications such as atherosclerosis, diabetic retinopathy, nephropathy, neuropathy, micro- and macroangiopathy, immune system disorders, let alone the possibility of developing of life-threatening various types of diabetic coma.
The main goal of treatment of diabetes of any type is to achieve the compensation of carbohydrate metabolism. Full compensation of metabolism enables to provide normal growth and development of children who suffer from diabetes, prevent the development of acute and chronic complications, maintain and restore patient’s workability, improve their quality of life, normalize body weight.
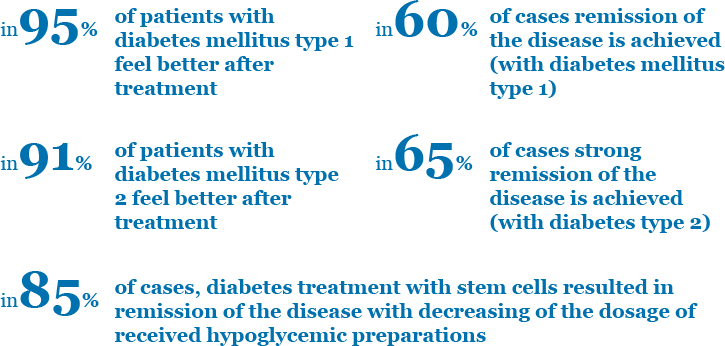
Unique Cell Treatment Clinic (UCTC) has developed schemes of comprehensive treatment of diabetes of any type based on fetal stem cells, which influence the pathogenesis of this disease, they are the following:
1) transform into β-cells of the pancreas, thus restoring synthesis and insulin release;
2) replace inadequate immune system cells, dramatically reducing and sometimes completely eliminating an autoimmune component of the disease, stopping the destruction of β-cells and preventing further progression of the disease and the development of secondary complications of the infectious nature;
3) replenish stem reserves for regeneration and repair of damaged tissues of the body by stimulating its own regenerative resources under the influence of growth factors produced by the cells;
4) stimulate the "renewal" of the damaged intima of blood vessels (angiogenesis), which plays a leading role in the development of additional vascular collaterals, improving tissue trophism.
Cell therapy is the only existing for today effective pathogenetic treatment of diabetes, as well as prevention and treatment of diabetes complications:
diabetic nephropathy (chronic renal failure)
After treatment with medications based on fetal cell suspensions such effects are noticed in patients with diabetes:
 |
Due to the significant decrease of blood glucose level positive dynamics of clinical disease is observed, making it possible to improve the quality of life of the patient, keep working. |  |
Stable remission of disease is achieved, making it possible to reduce the dosage or completely withdraw from taking hypoglycemic medications (insulin or tablet forms of drugs). |
 |
Long-term compensation of carbohydrate metabolism helps to prevent the occurrence or further progression of chronic complications of diabetes by kidneys, eyes, cardiovascular and nervous system. |  |
Full control of glycemia, as well as concomitant strengthening effect on the immune system of the body reduces the risk of associated acute and chronic diseases of infectious nature. |
