Liver cirrhosis treatment and chronic hepatitis treatment
For almost twenty years, specialists of the Unique Cell Treatment Clinic have been developing and applying effective methods of treatment of liver diseases and their complications.
The liver is one of the most important human organs that performs a variety of functions. The main function of the liver is neutralization and excretion of toxic substances coming from the external environment (various allergens, toxins, alcohol, drugs) or formed in the body due to metabolism (acetone, ammonia, ethanol and others). The liver is involved in the metabolism, digestion, regulation of carbohydrate metabolism, it is a depot of microelements, vitamins and glycogen, the liver also synthesizes blood proteins involved in blood clotting and transportation of various vitamins and hormones throughout the body.
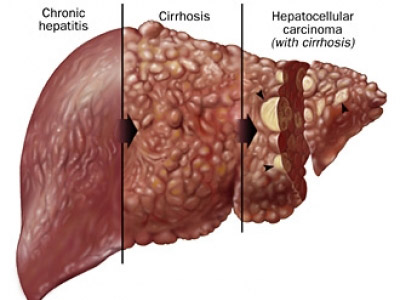 The most common diseases of the liver are hepatitis and cirrhosis.
The most common diseases of the liver are hepatitis and cirrhosis.
Hepatitis is characterized by development of acute or chronic diffuse liver inflammation of various origins. The most common is hepatitis of infectious etiology (viral hepatitis A, B, C, D, E, F, G) and toxic hepatitis (alcoholic, drug-induced, in case of chemicals poisoning). Also hepatitis may be developed in case of various autoimmune diseases and X-ray sickness. The acute form of inflammation is usually observed in case of viral hepatitis and poisoning. The outcome of the disease is either a full recovery, or transition from acute form of the disease into a chronic one (developing more than 6 months).
Initially chronic form of hepatitis can be developed independently (for example, due to prolonged alcohol intoxication) or due to the past acute hepatitis (most often viral hepatitis B, C, D and G). Untreated chronic hepatitis is dangerous because of probable developing of the liver cirrhosis and a high risk of developing of the liver cancer.
Cirrhosis is characterized by irreversible substitution of liver cells (hepatocytes) by connective tissue. A syndrome of hepatocellular failure develops, leading to a complete disruption of the normal functioning of the organ, and the so-called portal hypertension syndrome. If chronic hepatitis could be efficiently treated (although some its forms with difficulties), to get rid of the liver cirrhosis is possible only by organ transplantation. Conventional treatments are able only to slow down the progression of the disease and to reduce the risk of life-threatening cirrhosis complications (portal hypertension, gastrointestinal bleeding, hepatic encephalopathy (coma), bacterial ascites-peritonitis, portal vein thrombosis, hepatorenal syndrome, hepatocellular carcinoma).
Developed by Professor Smikodub and carried out in the Unique Cell Treatment Clinic stem cell therapy for liver diseases is pathogenic, it effectively treats pathological changes in the body, emerging due to negative impact of viruses, toxins, alcohol, etc. Cell therapy is applied in combination with the newest methods of etiotropic therapy affecting the reason of the disease (for example, antiretroviral therapy of chronic hepatitis B and C with interferon).
Fetal stem cells come into the zone of hepatocytes death, form new pools (groups) of cells capable to settle down and function for a long time, thereby replacing the affected liver cells by healthy ones. At that occurs regeneration of hepatic tissue, leading to the restoration of its functions.
During the treatment by transplantation method, several millions of fetal stem cells which passed primary differentiation are administered into a human's body; these cells turn into hepatocytes, restoring the liver function. Fetal stem cells also produce biologically active substances that stimulate the division of their own stem cells and thereby renew the cellular structure of the sick organ. Stem cells normalize and stimulate functioning of the immune system and all internal organs - the patient receives tremendous energy to cope with the disease.
Due to biologically active substances, during the first hours and days after transplantation patients note improving of emotional state, reducing of depression, improving of memory and thinking, normalizing of sleeping. In result of stem cell therapy significant improvement of blood values characterizing the liver function (bilirubin, ALT, AST, GGT, ALP, total protein, albumin, platelets) is seen, the risk of developing of cirrhosis complications such as portal hypertension or bleeding is reduced.
Of course, the success of treatment of viral hepatitis and liver cirrhosis depends on the type of virus (in case of chronic hepatitis C - also its genotype), duration of the disease, amount of virus and transaminase levels (ALT and AST) in blood.
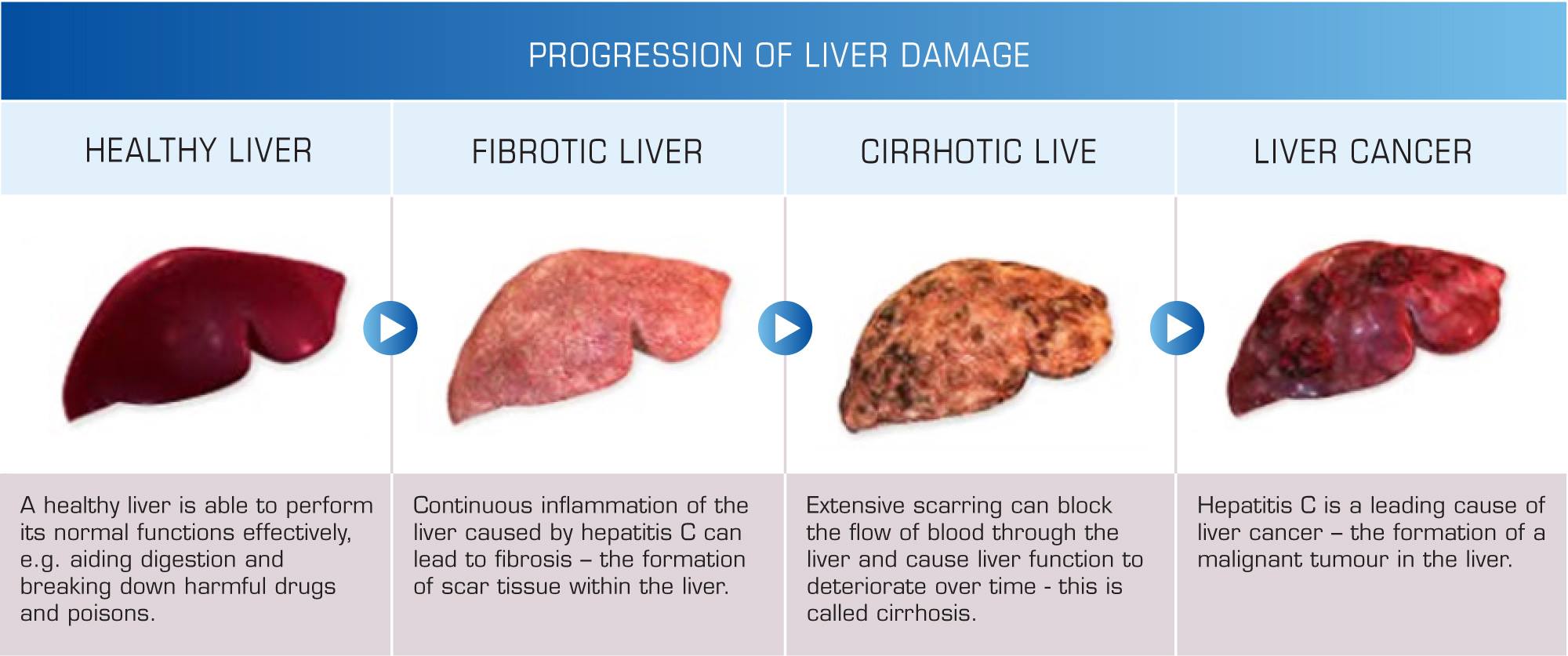
According to our experience, the best results are achieved when the treatment with fetal stem cells is started at the earlier stages of the disease. Fetal stem cells treatment by method of Prof. Smikodub is equally effective for any ethiology of liver disease and allows to achieve the results that are far superior to the most modern pathogenetic treatments of chronic hepatitis and liver cirrhosis. It can significantly improve the overall condition of the patient, quality of life, to move aside the deadly threat.
Cell treatment in most cases is easily tolerated by the patient and lasts from 3 to 5 days depending on the severity of the patient’s condition.
Results of the treatment for patients with liver disease:
 |
Asthenic syndrome symptoms decline Disappearance of vegetative asthenic syndrome symptoms - fatigue, performance decrement, irritability, drowsiness, dizziness, headaches |
 |
Gastrointestinal problems disappear Gastrointestinal symptoms such as nausea, bitter and unpleasant taste in the mouth, bloating, discomfort or pain in the right upper hypochondrium, especially after meals, altered defecation pattern disturb much more rarely |
 |
Intoxication syndrome decreases Reduction of the manifestation of intoxication syndrome: dryness and itching of skin, ochrodermia, pain in joints and muscles |
 |
Bleeding complications stop The appearance of bleeding complications - bleeding from the gums and hemorrhoids, easy development of subcutaneous hemorrhages ("bruises") reduces |
